Speed Comparison: C++, generic C++, D, generic D
Posted on: April 15, 2008
- In: Programming
- 1 Comment
So I wondered in which programming language I should write my next project.There
are two cool sites that compare programming languages:
The source code for different tasks: http://rosettacode.org/wiki/Generic_swap
The speed/memory consumption/compile time: http://shootout.alioth.debian.org/gp4/benchmark.php?test=all〈=all
For small projects I’d always use Python and extend it with C++ using Boost:Python (which works exceptionally well once you get to know it, but takes ages to figure out). However, I think it is better to program the whole core functionality in a statically typed language such that it can easily wrapped and used for example in Python.
The D programming language looks really nice and it also shows up quite high on the benchmark (on linux on second place). So I wondered how it performs speedwise to C++. So I copied some example from the web, the bubble sort problem and implemented it four times:
- c++
- generic c++
- D
- generic D
The code is below.
Turns out that the C++ code is approximately twice as fast as the D code which
disqualifies D for me at the moment. Also, there is practically no speed gain
for the templated implementation in D.
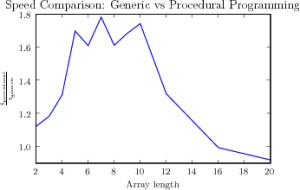
So for the comparison of C++ and templated C++ code I obtained.
Its hard to read, but on the y-axis the relative speedgain of the templated
version is plotted. So if your array is longer than 16, the templated version
is even slower than the normal. I actually expected some kind of monotonic
decay. Couldnt figure out why there is a max around array length = 8.
/*****************************************
A comparison between different implementations
of the Bubble sort algorithms. The question is: How much faster is the algorithm with template programming.
Examples inspired by http://ubiety.uwaterloo.ca/~tveldhui/papers/Template-Metaprograms/meta-art.html written by Todd Veldhuizen
*****************************************/
/*****************************************
OUTPUT:
> ./bubblesort
0.027000, 0.030000, 0.128000, 0.016000, 0.016000
*****************************************
#include
#include
#include <SDL.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
using namespace std;
/* isn't actually used, we use the SDL timer instead,
it gives the same results */
int mtime(void)
{
timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv,NULL);
return (int)(tv.tv_sec*1000 + (tv.tv_usec / 1000));
}
void print_vec(vector &v, string description)
{
printf("%s\t",description.c_str());
printf("[ ");
for(int i = 0; i< v.size(); ++i)
{
printf("%d ",v[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
}
inline void swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int tmp = a; a = b; b = tmp;
}
/* straight forward implementation of Bubblesort */
void bubbleSort1(int *data, int N)
{
for(int i = N-1; i > 0; --i)
{
for(int j = 0; j<i; ++j)
{
if(data[j] > data[j+1])
{
swap(data[j], data[j+1]);
}
}
}
}
/* recursive Bubble sort, one for loop replaced by recursion */
void bubbleSort2(int *data, int N)
{
for(int j = 0; j < N-1; ++j)
{
if(data[j] > data[j+1])
swap(data[j], data[j+1]);
}
if (N>2)
bubbleSort2(data, N-1);
}
/* recursive recursive Bubble sort, both loops replaced by recursion */
void bubbleSortLoop3(int *data, int N)
{
if (N>1)
bubbleSortLoop3(data, N-1);
if(data[N-1] > data[N])
swap(data[N-1],data[N]);
}
void bubbleSort3(int *data, int N)
{
bubbleSortLoop3(data, N-1);
if (N>2)
bubbleSort3(data, N-1);
}
/* template metaprogramming Bubble sort */
template class tswap
{
public:
static inline void compareAndSwap(int* data)
{
if (data[I] > data[J])
swap(data[I], data[J]);
}
};
template class tbubbleSortLoop
{
public:
static inline void loop(int *data)
{
tbubbleSortLoop::loop(data);
tswap<N-1,N>::compareAndSwap(data);
}
};
template<>
class tbubbleSortLoop
{
public:
static inline void loop(int *data)
{
tswap<0,1>::compareAndSwap(data);
}
};
template
class tbubbleSort
{
public:
static inline void sort(int *data)
{
tbubbleSortLoop::loop(data);
tbubbleSort::sort(data);
}
};
template<>
class tbubbleSort
{
public:
static inline void sort(int *data)
{
tbubbleSortLoop::loop(data);
}
};
/* Todd Veldhuizens reference implementation */
template
class IntSwap
{
public:
static inline void compareAndSwap(int* data)
{
if (data[I] > data[J])
swap(data[I], data[J]);
}
};
template
class IntBubbleSortLoop
{
private:
enum { go = (J <= I-2) };
public:
static inline void loop(int* data)
{
IntSwap<J,J+1>::compareAndSwap(data);
IntBubbleSortLoop::loop(data);
}
};
template<>
class IntBubbleSortLoop<0,0>
{
public:
static inline void loop(int*)
{ }
};
template
class IntBubbleSort
{
public:
static inline void sort(int* data)
{
IntBubbleSortLoop<N-1,0>::loop(data);
IntBubbleSort::sort(data);
}
};
template<>
class IntBubbleSort
{
public:
static inline void sort(int* data)
{ }
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
/*generate array */
const int N = 4; /* array length */
const int NUMBER_OF_SORTS = 2000000;
Uint32 start,end; /* for timing */
vector original_data(N*NUMBER_OF_SORTS);
for(int j = 0; j < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++j)
{
for(int i = 0; i < N ; ++i){
original_data[i+N*j] = N-i;
}
}
vector data(original_data);
/* bubbleSort1 */
data = original_data;
start = SDL_GetTicks();
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++i)
{
bubbleSort1(&data[i*N],N);
}
end = SDL_GetTicks();
printf("%f,\t",(end-start)/1000.);
/* bubbleSort2 */
data = original_data;
start = SDL_GetTicks();
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++i)
{
bubbleSort2(&data[i*N],N);
}
end = SDL_GetTicks();
printf("%f,\t",(end-start)/1000.);
/* bubbleSort3 */
data = original_data;
start = SDL_GetTicks();
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++i)
{
bubbleSort3(&data[i*N],N);
}
end = SDL_GetTicks();
printf("%f,\t",(end-start)/1000.);
/* templated bubbleSort */
data = original_data;
start = SDL_GetTicks();
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++i)
{
tbubbleSort::sort(&data[i*N]);
}
end = SDL_GetTicks();
printf("%f,\t",(end-start)/1000.);
/* templated bubbleSort, Todd Veldhuizens reference implementation */
data = original_data;
start = SDL_GetTicks();
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++i)
{
IntBubbleSort::sort(&data[i*N]);
}
end = SDL_GetTicks();
printf("%f\n",(end-start)/1000.);
return 0;
}
/**************************************
OUTPUT:
> ./D_bubblesort
straight forward implementation
0.058
recursive implementation
0.071
templated implementation
0.062
testing static array filling
[ 0 1 2 3 4 ]
**************************************/
//compile with dmd -O -inline -release D_bubblesort.d
version(Win32){
/*
* GetTickCount() wraps after 47 days or so, but this does
* not matter, as we use unsigned for creating the difference.
*/
private import std.c.windows.windows;
static int
diffmtime(inout DWORD old){
int Result;
DWORD now = GetTickCount();
Result = now - old;
old = now;
return Result;
}
}
version(linux){
/*
* On linux, we could run with higher resulution,
* but we don't
*/
private import std.c.linux.linux;
static int
diffmtime(inout timeval old){
int Result;
timeval now;
gettimeofday(&now,null);
/* Convert to msec */
Result = (now.tv_sec-old.tv_sec)*1000
+(now.tv_usec-old.tv_usec)/1000 ;
old = now;
return Result;
}
}
import std.stdio;
void print_vec(in int v[], string description="")
{
writef("[ ");
for(int i = 0; i< v.length; ++i)
{
writef("%d ",v[i]);
}
writef("]\n");
}
/* NORMAL IMPLEMENTATION */
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp;
}
/* straight forward implementation of Bubblesort */
void bubbleSort1(int *v, int N)
{
for(int i = N; i > 0; --i)
{
for(int j = 0; j<i; ++j)
{
if(v[j] > v[j+1])
swap(&v[j], &v[j+1]);
}
}
}
/* recursive implementation of Bubblesort */
void bubbleSortLoop2(int *data, int N)
{
if (N>1) bubbleSortLoop2(data,N-1);
if(data[N-1] > data[N])
swap(&data[N-1], &data[N]);
}
void bubbleSort2(int *data, int N)
{
bubbleSortLoop2(data, N-1);
if (N>2)
bubbleSort2(data,N-1);
}
/* TEMPLATED IMPLEMENTATION OF ARRAY INITIALIZATION */
template a(int N)
{
static void fill(int *data){
static if(N>=0)
{
a!(N-1).fill(data);
data[N] = N;
}
}
}
/* TEMPLATED IMPLEMENTATION OF BUBBLESORT */
template tswap(int I, int J)
{
static void perform(int *data){
if(data[I] > data[J])
{
swap(&data[I],&data[J]);
}
}
}
template tbubbleSortLoop(int N)
{
static void perform(int *data)
{
static if(N>1) tbubbleSortLoop!(N-1).perform(data);
tswap!(N-1,N).perform(data);
}
}
template tbubbleSort(int N)
{
static void perform(int *data)
{
tbubbleSortLoop!(N-1).perform(data);
static if(N>2) tbubbleSort!(N-1).perform(data);
}
}
class Foo
{
template TBar(T)
{
static T yy; // Ok
static int func(T t, int y)
{
return 0; // Ok
}
}
}
template Factorial(ulong n)
{
static if( n <= 1 )
const Factorial = 1;
else
const Factorial = n * Factorial!(n-1);
}
int main()
{
const int N = 4;
/* array length */
const int NUMBER_OF_SORTS = 2000000;
timeval t;
/* fill some array */
int[] original_data;
original_data.length = N*NUMBER_OF_SORTS;
for(int j = 0; j < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++j)
{
for(int i = 0; i < N ; ++i)
{
original_data[i+N*j] = N-i;
}
}
writefln("straight forward implementation");
int[] data = original_data.dup;
gettimeofday(&t,null);
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++i)
{
bubbleSort1(&data[i*N],N);
}
writefln(diffmtime(t)/1000.);
writefln("recursive implementation");
data = original_data.dup;
gettimeofday(&t,null);
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++i)
{
bubbleSort2(&data[i*N],N);
}
writefln(diffmtime(t)/1000.);
writefln("templated implementation");
data = original_data.dup;
gettimeofday(&t,null);
for(int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_SORTS; ++i)
{
tbubbleSort!(N).perform(&data[i*N]);
}
writefln(diffmtime(t)/1000.);
writefln("testing static array filling");
int[] lala;
lala.length=5;
a!(5).fill(&lala[0]);
print_vec(lala);
return 0;
}
April 26, 2008 at 11:09 pm
Note the benchmarks game also shows full source code and build & run logs for all the programs, for example
http://shootout.alioth.debian.org/gp4/benchmark.php?test=spectralnorm&lang=nice&id=0